A single power source and a single reactor
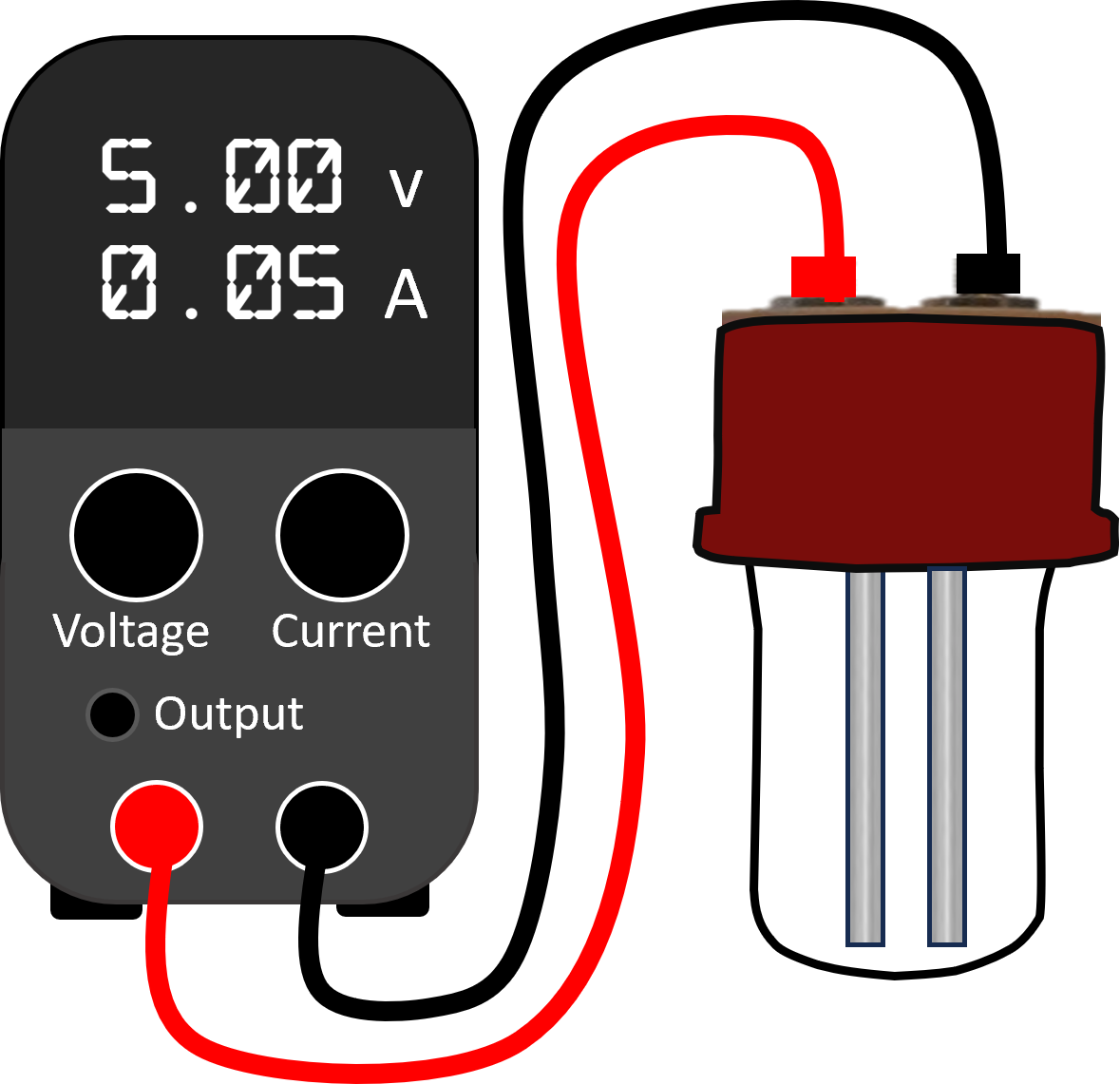 Running a single reactor with a single powersupply is straight forward - you wire the two electrodes and set the powersupply to run under conditions of constant current or constant voltage. With the former, as the resistance of the solution changes through the reaction the powersupply will vary the voltage to maintain the current. Under constant voltage, the powersupply will vary the current to maintain the voltage. Generally you can directly read off the powersupply the instantaneous parameters (or can data-log, allowing you to calculate the total energy for the reaction).
Running a single reactor with a single powersupply is straight forward - you wire the two electrodes and set the powersupply to run under conditions of constant current or constant voltage. With the former, as the resistance of the solution changes through the reaction the powersupply will vary the voltage to maintain the current. Under constant voltage, the powersupply will vary the current to maintain the voltage. Generally you can directly read off the powersupply the instantaneous parameters (or can data-log, allowing you to calculate the total energy for the reaction).
Running multiple reactors off a single power supply
For screening, you may want to run multiple reactors to give a greater throughput. These reactors can be wired in series or in parallel, with the powerpack running under constant current or constant voltage mode. Lets look at what this means. For the examples below, we have just used 2 reactors, but similar principles apply to multiple reactors.
With series wiring, each reactor will have the same current flowing through it. It is quite likely that the resistance of each reactor will be different (and possibly vary during the course of the reaction). The potential difference across each reactor will be different. For more reactors in series, the current through each will be the same.
With parallel wiring, each reactor will have the same potential difference across it. It is quite likely that the resistance of each reactor will be different (and possibly vary during the course of the reaction). The current that flows through each reactor will be different. For multiple reactors in parallel, the potential difference across each reactor will be the same, but the current will be different.
The modeller below helps you understand this.
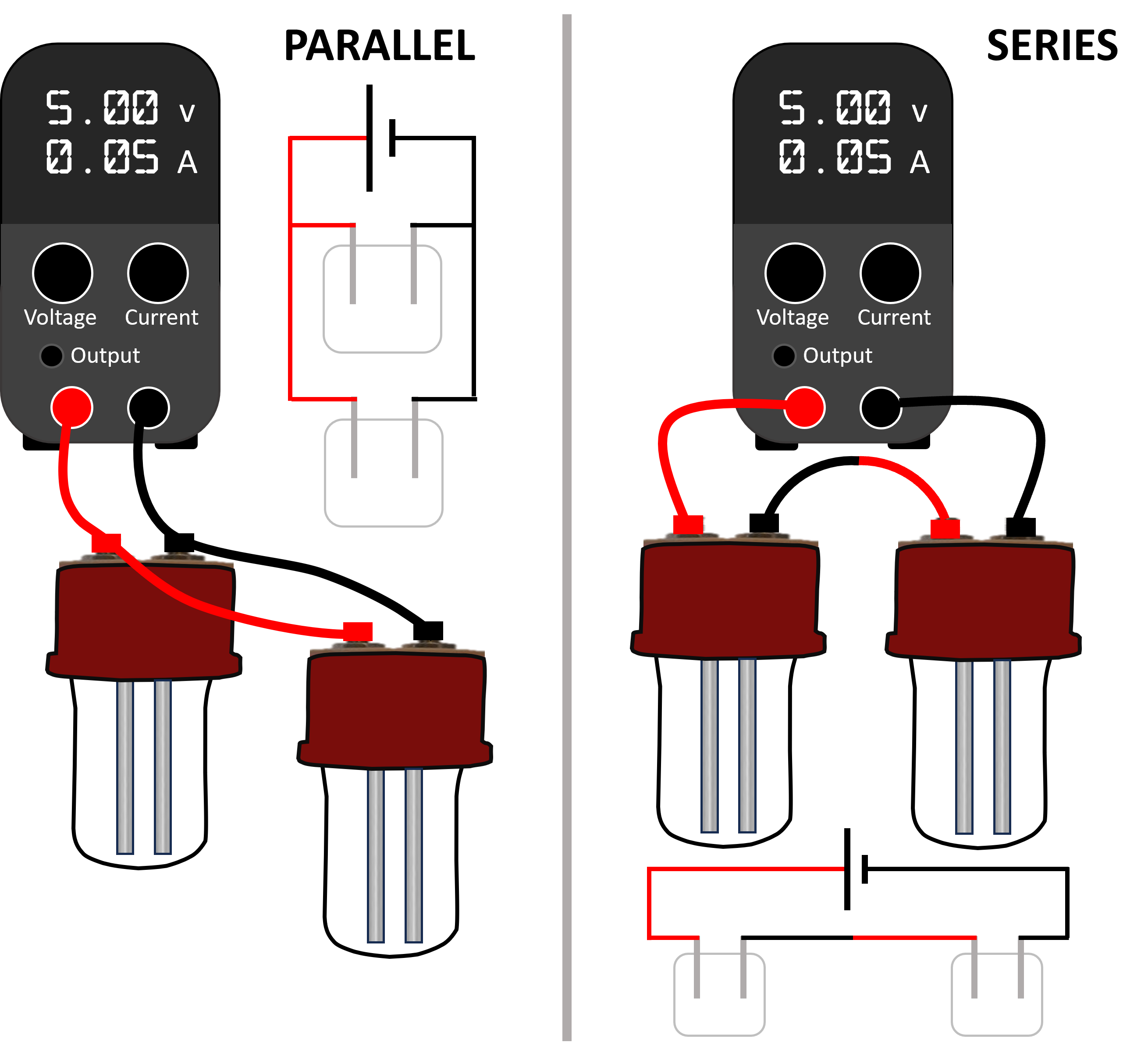
This modeller helps you understand the flow of current and the potential difference in reactors wired in parallel or series. The relative resistance setting represents the ratio of resistance in the first reactor to the second (a value greater than 1 means the resistance is greatest in reactor one, a value lower than 1 means the resistance is lower in reactor one).
